What is Germination?
Germination is the process of an organism growing from a seed, in the span of two (2) weeks. And other
seeds taking longer than two weeks.
Conditions for Germination
There are three necessities for germination they are:
Water-is crucial for germination in mature seeds, as they need enough water to moisten but not to soak them. This process is called imbibition, which causes the seed coat to break down stored food resources into metabolically useful chemicals. After the seedling emerges from the seed coat, photosynthesis provides energy, and the seedling requires a continuous supply of water, nutrients, and light.
Oxygen-is also required for metabolism, and some seeds have impermeable seed coats that prevent oxygen from entering the seed, causing physical dormancy. In some plants, such as rice, anaerobic germination can occur in waterlogged conditions. Temperature affects cellular metabolic and growth rates, with some seeds germinating at slightly above 60-75 F (16-24 C), while others germinate just above freezing or in response to temperature alternations between warm and cool conditions.
Temperature-significantly impacts cellular metabolic and growth rates, with seeds germinating over a wide range. Some germinate at slightly above 60-75 F (16-24 C), while others germinate just above freezing. Some seeds require cold temperatures to break dormancy, while others will not germinate even if favorable conditions are favorable. Some seeds require cold stratification to break dormancy before light emission, promoting germination. Some seeds, like Ranunculaceae, require conditions cooler than -5 C. Physical dormancy occurs when seeds are exposed to hot temperatures during a forest fire.
Process of Germination
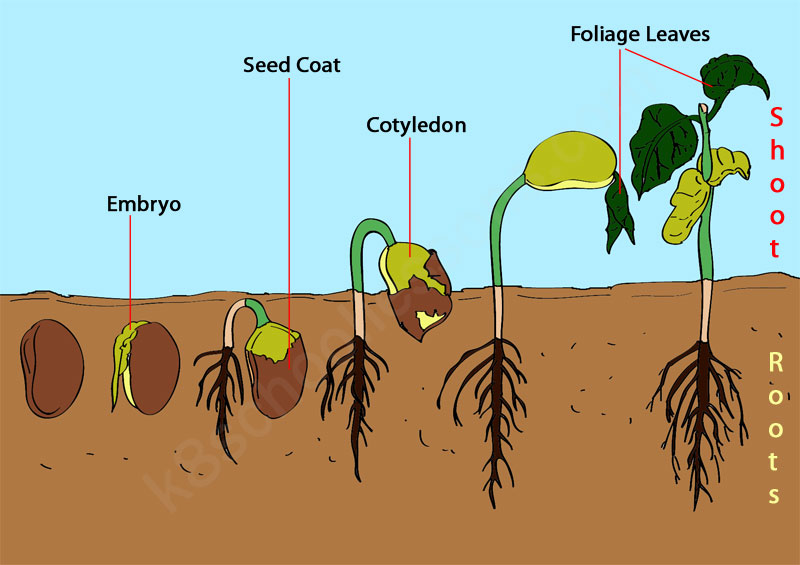
The importance of Germination
Germination is important because it determines the continuous production of food for human survival.